
Neurologic – confusion, dysarthria, nystagmus, lethargy, ataxia, areflexia, hypotonia, seizure.
Calculate the maximum possible dose per kg of each drug.If possible, determine the exact name and tablet strength.Always assume maximum number of missing/unaccounted tablets have been ingested.Risk assessment Red flag features in Red History Diazepam is excreted mainly (about 70%) unchanged in the urine.Īll children with deliberate self-poisoning or significant accidental ingestion, especially younger children and toddlers.Īny child whose developmental age is inconsistent with accidental poisoning as non-accidental poisoning should be considered.An exception to this is Oxazepam, temazepam, and lorazepam which are directly conjugated.Drugs that interact with CYP enzymes may prolong the half-lives of most Benzodiazepines
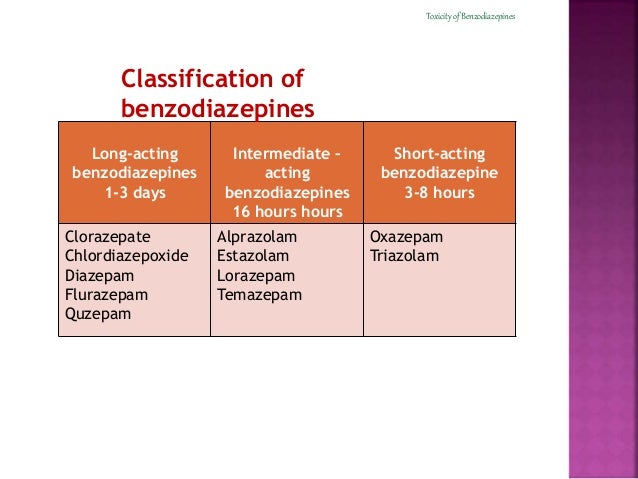
 They are rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations occurring 30 to 90 minutes after ingestion. Short-acting (half-life 24 h) eg Diazepam, these generally have pharmacologically active metabolites, accumulate in tissues after multiple doses, and demonstrate impaired clearance in children with liver disease. Benzodiazepines can be short, intermediate or long acting:. Sedation can be prolonged and last up to 36 hours. All intentional overdoses require a Mental Health Assessment.įor 24 hour advice, contact Victorian Poisons Information Centre 13 11 26 Background. Close observation and supportive care are the mainstay of management. Pure benzodiazepine overdoses usually induce a mild to moderate central nervous system depression deep coma requiring assisted ventilation is rare, and should prompt a search for other toxic substances. Poisoning – Acute guidelines for initial management Coma Afebrile Seizures Resuscitation Key points
They are rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations occurring 30 to 90 minutes after ingestion. Short-acting (half-life 24 h) eg Diazepam, these generally have pharmacologically active metabolites, accumulate in tissues after multiple doses, and demonstrate impaired clearance in children with liver disease. Benzodiazepines can be short, intermediate or long acting:. Sedation can be prolonged and last up to 36 hours. All intentional overdoses require a Mental Health Assessment.įor 24 hour advice, contact Victorian Poisons Information Centre 13 11 26 Background. Close observation and supportive care are the mainstay of management. Pure benzodiazepine overdoses usually induce a mild to moderate central nervous system depression deep coma requiring assisted ventilation is rare, and should prompt a search for other toxic substances. Poisoning – Acute guidelines for initial management Coma Afebrile Seizures Resuscitation Key points







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
